Day 1
4.5.20
Good Morning Boys,
Today we will discuss about the shapes of Atomic orbital, energies of orbital and rules for filling of electron in the orbitals of atom.
Learning Objective :
students will be able to


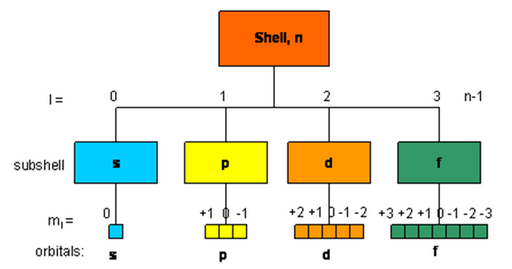
The order in which the orbitals are filled is as follows:
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s...
4.5.20
Good Morning Boys,
Today we will discuss about the shapes of Atomic orbital, energies of orbital and rules for filling of electron in the orbitals of atom.
Learning Objective :
students will be able to
- Draw the shapes of various atomic orbital.
- understand the concept of degenerate orbitals.
- Learn the rules for filling electron in atom.
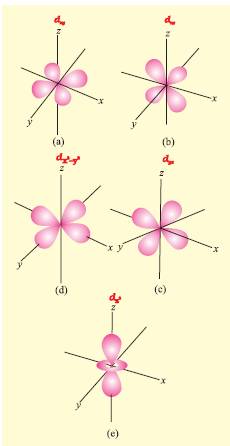
Shapes of Orbital:

- s orbital: Spherical in shape, non-directional. It has only 1 orbital therefore, can accommodate only 2 electrons.

- p-orbital: dumb-bell shaped and directional. It has 3 orbital i.e px, py, pz.(p–orbital have three different orientations. These are designated as px, py & pz depending upon whether the density of electron is maximum along the x y and z axis) It can accommodate maximum of 6 electrons.

- d-orbital: It is double dumbbell shaped, directional. It has 5 orbital (dxy,dyz,dzx,dx2-y2,dz2).Out of the five orbitals, the three (dxy, dyz, dzx) project in between the axis and the other two dz2 and dz2-y2 lie along the axis. It can accommodate maximum of 10 electrons

- f-orbital: It has diffused shape. It has 7 orbital therefore, can accommodate maximum of 14 electrons.
Points for reference :
1. Shielding effect or screening effect:
Due to the presence of electrons in the inner shells, the electron in the outer shell will not experience the full positive charge of the nucleus. So, due to the screening effect, the net positive charge experienced by the electron , from the nucleus (effective nuclear charge ) is lowered .
2. Nodal surfaces /Nodal Points and Planes or simply nodes :
The point where there is zero probability of finding the electron is called nodal point. There are two types of nodes: Radial nodes and angular nodes.Radial nodes is concerned with distance from the nucleus.Angular is concerned with direction.No. of radial nodes = n – l – 1No. of angular nodes = l Total number of nodes = n – 1Nodal planes are the planes of zero probability of finding the electron. The number of such planes is also equal to l.
Degenerate orbitals: Orbitals having the same energy are called degenerate orbitals. Shape of p and d-orbitals.
Rules For Filling electron in orbitals of atom :
Aufbau Principle:
In the ground state of the atoms, the orbitals are filled in order of their increasing energies.
The order in which the orbitals are filled is as follows:
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s...
the direction of the arrow gives the order of filling of orbitals.
Note :
n+l rule-
Orbitals with lower value of (n+l) have lower energy.
If two orbitals have the same value of (n+l) then orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Pauli Exclusion Principle:
"No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers."
Only two electrons may exist in the same orbital and these electrons must have opposite spin.
Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity:
Pairing of electrons in the orbitals belonging to the same subshell (p, d or f) does not take place until each orbital belonging to that subshell has got one electron each i.e., it is singly occupied.
( This is due to the fact that electrons being identical in charge, repel each other when present in the same orbital. This repulsion can, however, be minimized if two electrons move as far apart as possible by occupying different degenerate orbitals. All the electrons in a degenerate set of orbitals will have same spin. )
Mark your attendance on the form as well as comment section of blog.

Anshuman Jaison of 11D is present
ReplyDeleteAaron Isaac Khakha
ReplyDelete11D
Present
Ma'am not able to understand
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am,
ReplyDeleteYumn Jame 11th D present.
Tanmay Jain
ReplyDelete11-D
Present
Good Morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteAmit S Sahu,11-D
Present
Sushant Kumar 11D prese
ReplyDeletePresent
DeleteGood morning ma'am. This is Shambhava S. of 11D!
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteArtham Pedneker 11-D
present
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSamarth Jain
11 D
Present
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteAnugrah Singh 11D
Present
Anugrah Steve Massey 11D present
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteBhumik Tandon of class 11th D is present
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSarvesh Kumar
11 D
is Present
Aashish Parker XI-D Present
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSami ansari 11-D
Present
ADITYA VOHRA 11-d present
ReplyDeleteGood Morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSuchit Bhatnagar 11-D
Present
Siddharth Karnish. 11-D
ReplyDelete(Present)
Tathastu Bagchi 11D present
ReplyDeleteTANUJ PANT
ReplyDelete11 D
Present
Tuhin Raha
ReplyDelete11-D
present
Albin G Koshy
ReplyDelete11-D
Present