
Day 3
17.4.20
Good morning Boys,
Today we will start with our first unit ,some basic concepts of chemistry.
Students are required to make one chemistry register where all the work related to the subject need to be noted. Register will be evaluated when the school reopens.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE :
students will be able
- Recall the S.I Units of Measurements
- Define matter
- Differentiate solid ,liquid and gases
Anything that has mass and occupies space is termed as matter.example:- notebook, pencil, air, water etc
Physical Classification of Matter
PropertiesSolidLiquidGas1. volumeDefiniteDefiniteIndefinite2. ShapeDefiniteIndefiniteIndefinite3. Inter molecular
force of attractionVery highModerateNegligible / Very
low4. arrangement of
moleculesOrderly arrangedFree to move
within the volumeFree to move every
where5. Inter molecular
spaceVery smallSlightly greaterVery great7. CompressibilityNot compressibleNot compressibleHighly
compressible8. Expansion on
heatingVery littleVery littleHighly expand9. RigidityVery rigidNot rigid knownas
fluidNot rigid and
known as fluid9. FluidityCan’t flowCan flowCan flow10. DiffusionThey can diffuse
due to kinetic energy of liquid/gasesCan diffuse And
rate of diffusion is very fastCan diffuse And
rate of diffusion is very fastChemical Classification of matter---
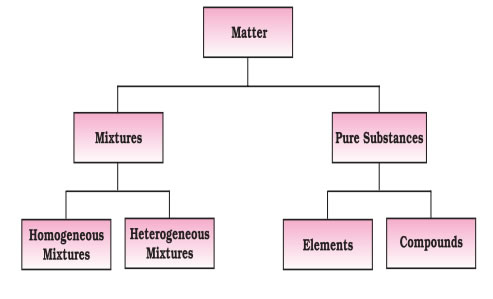
Pure Substances
- Pure substances have fixed composition, the constituents of pure substances cannot be separated by simple physical methods.
- Pure substances are further classified into elements and compounds.
- An element consists of only one type of particles. These particles may be atoms or molecules.
- For example: - Sodium (Na), copper (Cu). They contain only one type of atoms.
For example: - Water (H20), Ammonia (NH3).
Representation of atoms and molecules

- The properties of a compound are different from those of its constituent elements.
- Constituents of a compound cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical methods. They can be separated by chemical methods.
- A mixture contains two or more substances present in it in any ratio. Example:-Air
- mixture can be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
- homogeneous mixture, the components completely mix with each other and its composition is uniform throughout.
- For example: - Air, Sugar solution.
- heterogeneous mixtures,the composition is not uniform throughout and sometimes the different components can be observed ex sand m ixed with salt.
- The components of a mixture can be separated by using physical methods such as simple hand picking, filtration, crystallisation, distillation etc.
- Refer to the link for classification of matter :
- https://youtu.be/lUfNZ8tCTQc
- The International System of Units (SI)

- Mass is defined as the amount of matter present in a substance.
- Weight is defined as the force exerted by the gravity on an object.
- Density of a substance is its amount of mass per unit volume. SI unit of density = kg/m3.
- Temperature There are three common scales to measure temperature — °C (degree Celsius), °F (degree Fahrenheit) and K (kelvin). K is the SI unit.
- The temperatures on two scales are related to each other by the following relationship:-
- F = (9/5) (OC) + 32
- The Kelvin scale is related to Celsius scale as follows:-
- K =OC + 273.15
- Dalton's Atomic Theory
- • All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms.
- • Atoms of different elements are different in all respects.
- • Atom is the smallest unit that takes part in chemical combinations.
- •Atoms combine with each other in simple whole number ratios to form compound atoms called molecules.
- •Atoms cannot be created, divided or destroyed during any chemical or physical change.Atoms of the same element are identical in shape, size, mass and other properties.
Take care.
stay safe.
Pulkit Kohli 11-D present
ReplyDeleteJasKeerat (11-D) - Present
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am,
ReplyDeleteCelestine Saji,
11D
Tanmay Jain
ReplyDelete11-D
Present
Good morning
ReplyDeleteSushant Kumar 11D present
Good Morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteDhruv Ghoshal 11 D PRESENT
Ma'am do we need to note each and every thing.
ReplyDeletethis is just the elementary points .
Deleteplease write your name also to mark the attendance
SREYAS ADITYA BAKSI 11 D
ReplyDeletePRESENT
Sarvesh Kumar
ReplyDelete11-D is Present
Good Morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSuchit Bhatnagar 11-D is present
Ratnango Ghosh
ReplyDelete11 D Present
Tanuj pant of 11 D
ReplyDeletePresent
Good Morning. This is Shambhava S. from 11-D .
ReplyDeleteGood Morning
ReplyDeleteVatsal Aggarwal 11D
PRESENT
Aashish Parker XI-D Present
ReplyDeleteUtkrist Gupta
ReplyDelete11-D
Present
Lakshya Gunjan 11-D
ReplyDeleterishit gupta 11d present
ReplyDeleteArvin Prince 11D present
ReplyDeleteaarmaan chhibber 11d present
ReplyDeleteSiddharth Karnish
ReplyDelete11-D
Amal Roy Joseph of 11D US present
ReplyDeleteSoham Kulkarni
ReplyDelete11-D
Present Ma'am
Tathastu Bagchi of 11D is present
ReplyDeleteArmaan class 11th D present
ReplyDeleteMAM DO WE NEED TO NOTEDOWN EVERYTHING?
ReplyDeletethis is just the intro
DeleteGood Morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteTuhin Raha
11-D
present
good morning mam
ReplyDeletesami ansari 11D
preseny
ADITYA VOHRA 11-D present
ReplyDeletepresent
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteAvikam Gupta
11-D
Present
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteAnugrah Singh 11D
Present
Good Morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteUtsav Rajora 11D
Good Morning,
ReplyDeleteThis is Joseph James Nedumpara of XI D
Good morning
ReplyDeleteBhumik Tandon of class 11D is present
Good Morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteShaun Lawrence of class 11-D
Present
Maam is everything to be noted down? Please confirm
ReplyDeletethis is just the revision of topic previously learned.
Deletethis is upto you .
you can make flowchart of physical and chemical classification and note daltons theory
Good morning ma'am, this is Amit S Sahu from 11D
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSamarth Jain
11 D
Present
TEGHVEER SINGH
ReplyDeleteCLASS 11-D
PRESENT
good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteArtham Pedneker 11-D
present
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteYashas Yadav 11-D
Present
Ma'am do we have to copy the table and the flow chart in our registers
ReplyDeletetable ,flowchart and dalton theory
DeleteGood morning ma'am,
ReplyDeleteSatwik shrey
11D
Good morning ma'am,
ReplyDeleteYumn Jame 11 th D present.
Good morning
ReplyDeleteShreyansh Puri is present
Ma'am regarding the last point of Dalton's theory, doesn't nuclear fission lead to splitting of the nuclei of atoms? Does this contradict the theory, along with the fact that it was stated that atoms are the smallest particles...
ReplyDeleteThis is Shambhava S. of 11-D.
DeleteActually Shambava , the last postulate of the atomic theory stated in this blog has a minute error in it. The word DIVIDED isn't actually mentioned in the original postulate.
DeleteDalton theory was modified by number of scientist about whom you have learned in class 9 also. There were modification to each of the suggested theories about which we would be learning gradually.
DeleteAm i right Mr. Unknown ?
Yes maam . of course
DeleteThese were the assumptions which dalton formulated. however the discovery later have shown the existence of subatomic particles.
DeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSamuel DM 11-D
Present
Good morning. Anugrah Steve Massey 11D present
ReplyDeleteAlbin G Koshy
ReplyDelete11-D
Present
Mam the sequence is wrong there in the table of physical classification
ReplyDeleteDear student,
DeletePhysical classification is the classification of matter into its 5 states out of which we discuss solid, liquid and gases as per class 11 syllabus.
Shreyansh puri
ReplyDelete11-D
Lakshya Gunjan
ReplyDelete11-D