DAY 3
30.4.20
GOOD MORNING BOYS,
Today you will attend the MCQ FIRST then you will learn about Hydrogen spectrum and Bohrs theory.
30.4.20
GOOD MORNING BOYS,
Today you will attend the MCQ FIRST then you will learn about Hydrogen spectrum and Bohrs theory.
Students will be able to
- know different series in hydrogen spectrum
- learn Rydbergs formula
- understand Bohrs model for hydrogen atom.
Emission spectrum of
Hydrogen atom
Spectral Lines for atomic hydrogen is given by
Rydberg equation
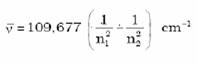
R = Rydberg’s constant = 109677 cm-1
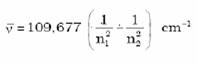
R = Rydberg’s constant = 109677 cm-1
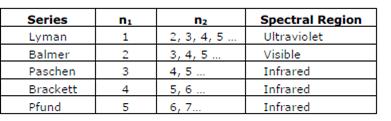
Bohr’s model for hydrogen atom:
Postulates
1. Electron in hydrogen atom moves around the nucleus in circular path of fixed radius and energy. These paths are called orbits or energy levels.
2. As long as an electron remains in a particular orbit, it does not lose or gain energy and its energy remains constant.
3. However, when electron will move from a lower stationary state to a higher stationary state a certain amount of energy is absorbed by the electron or some energy is emitted when electron moves from higher stationary state to lower stationary state
4. Frequency of radiations emitted or absorbed when transition of an electron occurs, is given by
5. An electron can move only in those orbits for which its angular momentum is an integral multiple of h/2π, i.e.,
[Where n =1,2,3.....]
Assumptions of Bohar’s model are:
1. The radii of the stationary states are expressed as:
2. Energy of an electron in nth orbit is given as:
Limitations of Bohr’s model of atom: 1. It failed to account for the finer details of the hydrogen spectrum.
2. It was unable to explain spectrum of atoms containing more than one electron.
3. It failed to explain splitting of the spectral lines in presence of electric (Stark effect) or magnetic field ( Zeeman effect).
4. It failed to explain formation of molecules from atoms by chemical bonding.
Dual behaviour of matter:
de Broglie proposed that matter exhibits dual behavior, i.e., matter shows both particle as well as wave nature and gave the following relation between wavelength (λ) and momentum (p) of a material particle.
[Where, m is the mass of the particle, v its velocity and p its momentum]
The above equation is named as de Broglie’s relation.
Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle:
Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle:
It states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously, the exact position and exact momentum (or velocity) of an electron. The product of their uncertainties is always equal to or greater than h/4π. I.e.,

Where, Δx = uncertainty in position
Δp = uncertainty in momentum
Significance of Uncertainty Principle
Significance of Uncertainty Principle
- Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle rules out the existence of definite paths or trajectories of electrons and other similar particles
- The effect of Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle is significant only for motion of microscopic objects and is negligible for that of macroscopic objects.
Reasons for the Failure of the Bohr Model:
1. It ignores the dual behavior of matter.
2. It contradicts Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle.
Thats all for the day
Take care
stay safe
MARK YOUR ATTENDANCE ON THE BLOG AS WELL AS FORM.
Aaron Isaac Khakha
ReplyDelete11D
Present
Jaskeerat Singh (11-D) - Present
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am,
ReplyDeleteYumn Jame 11th D present.
Good morning ma'am. The test and attendance has been submitted. -SHAMBHAVA S. (11D)
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteAnugrah Singh 11D
Present
Tuhin Raha
ReplyDelete11-D present
Good Morning Maam
ReplyDeleteRatnango Ghosh
11 D Present
Ma'am the above test is an MCQ, but on a particular question more than one answers are possible.
DeleteONLY ONE QUESTION HAS TWO ANSWERS FOR WHICH PARTICULAR CHOICE WAS GIVEN
DeleteAmit S Sahu 11 D present
ReplyDeleteMa'am, I had a doubt from the quiz.
DeleteIn the second question, when we use M1V1 = M2V2 then we get 200*.65 = x*.20 and the final volume comes as 650. But the question asks the amount of water that has to be added. So shouldn't the answer be 450 mL?
YES
DeleteCORRECT
THE ANSWER SHOULD BE 450 ML AS WATER QUANTITY IS ASKED
mam what is the difference between 1M and 1m
ReplyDelete1M is molarity and 1m molality
Deletem is for molality and M is for Molarity
DeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteRahul Bandhu
11D
Good morning ma'am,
ReplyDeleteCelestine Saji,
The test and the attendance has been submitted
Tathastu Bagchi 11D present
ReplyDeleteArtham Pedneker
ReplyDelete11-D
Present
Good Morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteSoham Kulkarni
11-D
Present
Siddharth Karnish. 11-D
ReplyDelete(Present)
Good evening
ReplyDeleteBhumikTandon of class 11th D is present
Attendence has been submitted on the form earlier